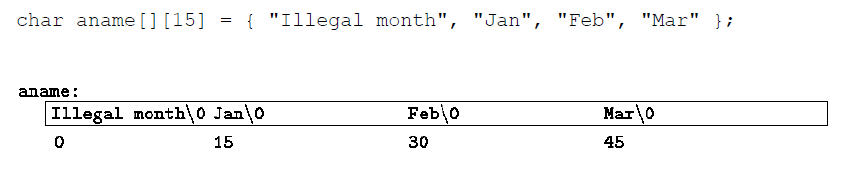Pointers and Arrays
Pointers and Addresses
- Address Of Operator
&can be applied to any memory object such as an array or a variable, not to any expression, constant, orregistervariable.
p = &c; //p stores address of c
//remember p is a pointer type variable
int *p; //pointer to an int, this says that value at *p is an int
- Dereferencing or Indirection -
*(value at) is the unary dereferencing operator and is used to access the value stored at a memory location.
*p = 0; //value at p = 0
- Some Tips
&and*have higher precedence than arithmetic operators.
++*ip; //increments value at ip
(*ip)++; //increments value at ip, parentheses are required here
iq = ip; //both are pointer variables to the same type, hence contents are copied into iq
Pointers and Function Arguments
- Call by Reference
swap(&a, &b);
void swap(int *x, int *y)
{
int temp;
temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
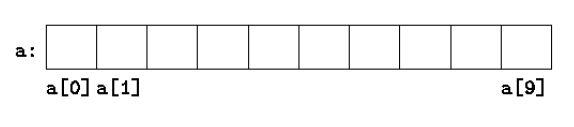
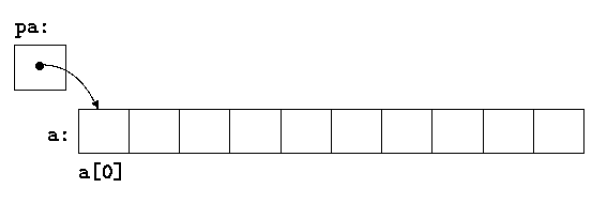
Pointers and Arrays
- An array name is equivalent to the pointer to the first element. Ex -
arris same as&arr[0].
int a[10];
int *p = &a[0];
//then to reach the ith element we can do -
int x;
x = *(p + i);
//this all is same as doing -
x = p[i];
The assignment p = &a[0]; is the same as p = a.
An arary name is not a variable so expressions like - arr = p and arr++ are illegal.
- As Function Parameter -
func(int a[]) {...}
//can also be written as -
func(int *a) {...}
Address Arithmetic
- Pointers can be added or subtracted with integer constants.
- Pointers from the same array (of the same type) can be subtracted.
- Pointers can be assigned to another pointer variable of the same kind.
- Pointers and integers are not interchangable with
0being an execption.
int *p = 0; //valid
if(*p == 0) //valid
//we can also use NULL defined in <stdio.h>
int *p = NULL;
- Pointer Comparisons are valid if they belong to the same array.
p < q; //this is true if p referes to an earlier element in an array, p and q must belong to the same array
- We cannot assign any pointer except
void*to the pointer of another type without a cast.
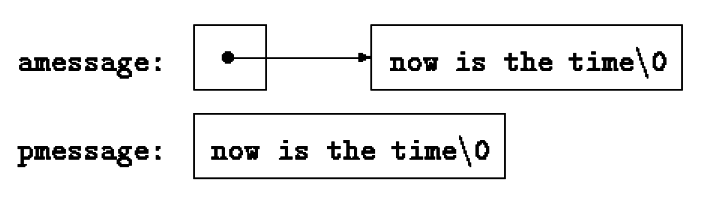
Character Pointers and Functions
char amessage[] = "now is the time"; /* an array */
char *pmessage = "now is the time"; /* a pointer */
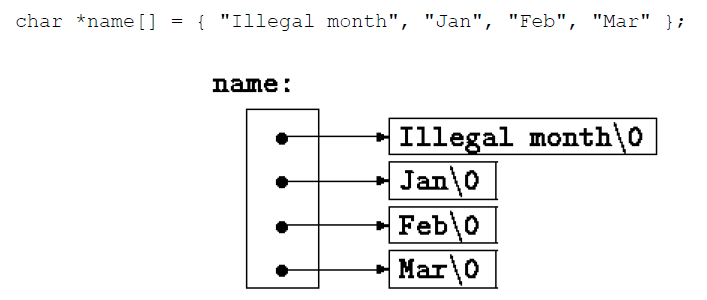
Pointer Arrays; Pointers to Pointers
- An array where each element is a pointer to another location.
Multi-dimensional Arrays
int arr[10][10]; //no. of rows = 10, no. of coloumns = 10
- A multi-dimensional array can be thought of as an array where each element is in itself an array.
- When passing a multi-dimensional array as function parameter -
int func(int arr[5][5]) { ... }
//or
int func(int arr[][5]) { ... }
//or
int func(int (*arr)[5]) { ... }
Only the first dimension can be skipped.
Initialization of Pointer Arrays
Pointer arrays have to be initialized before they can be used.
Pointers vs. Multi-dimensional Arrays
int a[10][20]; //Multi-dimensional array having 10 pointers, each pointing to array of 20 elements
int *b[10]; //pointer array of size 10, which can point anywhere
- Pointer arrays have an advantage that they can point anywhere and there is no storage that must be set aside unlike multi-dimensional arrays. This saves space.
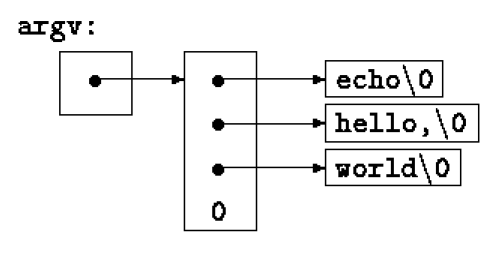
Command-line Arguments
-
In an environment using C, we can pass command-line arguments to a program when it begins executing.
-
int argc(argument count) andchar *argv(argument vector) are used for this. -
By convention, with
argv[0]a program is called soargc= 1. -
By convention,
argv[argc]is a null pointer (=0). -
echo hello, worldis represented as -
Pointer to Functions
- We can have pointer to functions and not use the signature with the pointer name as it is known throughout the program just like an array’s size.
int (*func)(); //pointer to function returning an integer