Structures
Definition
A structure is a collection of one or more variables, possibly of different types, grouped together under a single name for convenient handling.
Basics
-
A point is nothing but a pair of coordinates and a collection of points makes a rectangle.
-
structkeyword is used.
struct point {
int x;
int y; //members
};
An optional name called a structure tag may follow the word struct.
struct point {
int x;
int y;
} x , y, z;
- We can also declare
structtype variables.
struct point pt; //pt's type is struct point
//initialization can be done by
struct point pt = { 320, 200 };
- Accessing Members of a Structure -
structure-name . member
struct point pt;
int a = pt.x;
int b = pt.y;
- Structures can be nested as -
struct rect {
struct point pt1;
struct point pt2;
};
//we can declare screen as
struct rect screen;
//then
screen.pt1.x;
Structures and Functions
-
The only legal operations on structures are -
- Copying it
- Assigning to it
- Taking its address (&)
- Accessing its members (.)
-
Structure parameters are passed by value.
-
We can pass a pointer to a structure.
struct point *pp;
struct point origin;
*pp = &origin;
//to access elements
(*pp).x;
- Shorthand Notation - If pp is a pointer to a structure, then
// instead of writing this
(*pp).x;
// we can access members like this
pp -> x;
- Precedence of
->operator is the Highest.
struct point {
int x;
char *str;
} *p;
++ p -> x; // this increments x, not p
* p -> str; // this accesses location popinted to by str
Arrays of Structures
- Each element of array is a structure.
struct key {
int count;
char *word;
} keytab[NKEYS];
- Initialization -
Pointers to Structures
- A function can return a pointer to a
struct.
struct key *binsearch(int x, int y);
- Don’t assume that the size of a structure is the sum of sizes of its members.
struct {
char c;
int i;
}; //its size can be 8, not 5
sizeof() returns the exact value.
Self-referential Structures
- Used in recursively defined data structures like Trees.
struct node {
int value;
struct node *left;
struct node *right; //referring to self
}
Table Lookup
-
When a line like
#define IN 1is encountered, the name IN and the replacement text 1 are stored in a table. Later, when the name IN appears in a statement likestate = IN;it must be replaced by1. -
There are two routines that manipulate the names and replacement texts.
install(s,t)records the namesand the replacement texttin a table;sandtare just character strings.lookup(s)searches forsin the table, and returns a pointer to the place where it was found, orNULLif it wasn’t there. -
The algorithm is a hash-search - the incoming name is converted into a small non-negative integer, which is then used to index into an array of pointers. An array element points to the beginning of a linked list of blocks describing names that have that hash value. It is
NULLif no names have hashed to that value.
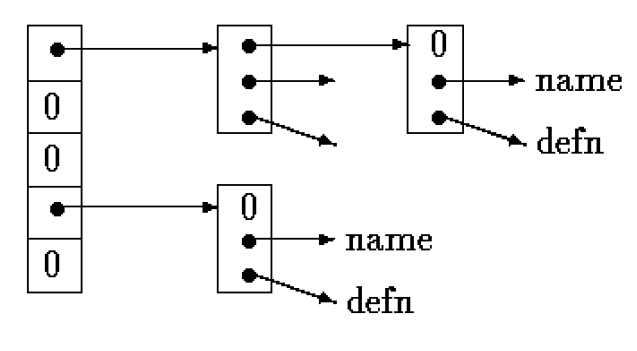
- A block in the list is a structure containing pointers to the name, the replacement text, and the next block in the list. A null next-pointer marks the end of the list.
struct nlist { /* table entry: */
struct nlist *next; /* next entry in chain */
char *name; /* defined name */
char *defn; /* replacement text */
};
Typedef
- We can create a new name for a data type using
typedef.
typedef int Length;
In the program that follows, we can use Length in place of int as a new type.
Length x, y;
typedefin C basically works as an alias.typedefcan be used to alias compound data types such as struct and union.typedefcan be used to alias both compound data types and pointer to these compound types.typedefcan be used to alias a function pointer.typedefcan be used to alias an array.
Unions
- A union is a variable that may hold multiple variables of any type and size.
union u_tag {
int ival;
float fval;
char *sval;
} u;
-
Accessing of members can be done as -
union-name . memberorunion-pointer -> member. -
The size of a union is big enough to hold the “widest” number.
-
Operations permitted are same as those of structures.
-
A union may only be initialized with a value of the type of its first member; thus union
udescribed above can only be initialized with an integer value.
Bit-fields
- A bit-field, or field for short, is a set of adjacent bits within a single implementation-defined storage unit that we will call a “word”.
struct {
unsigned int is_keyword : 1;
unsigned int is_extern : 1;
unsigned int is_static : 1;
} flags;
The number following the colon represents the field width in bits.
-
Individual fields are referenced in the same way as other structure members:
flags.is_keyword,flags.is_extern, etc. -
Almost everything about fields is implementation-dependent.