Memory and Files
Memory Management
Memory Layout
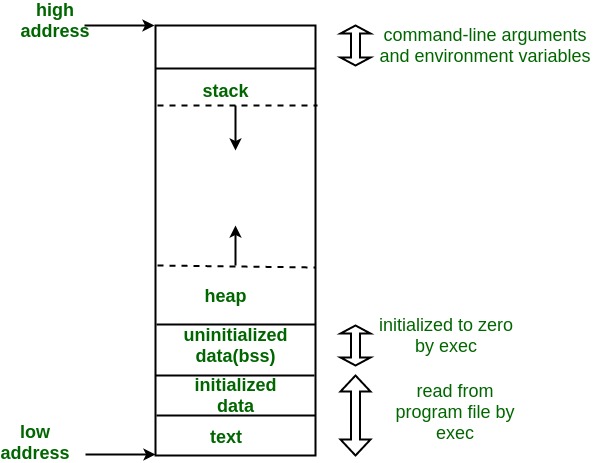
stack: funtion call stack, local variables
heap: dynamically allocated data objects
initialized data: global or static variables (initialized)
uninitialized data: global or static variables (uninitialized) a.k.a BSS (block started by symbol)
text: stores source code
// use size command to get memory layout
> size test.exe
Dynamic Allocation Fucntions
<stdlib.h>functions: returns pointer to allocated block orNULL.
- malloc(): memory allocation, fills with garbage
Syntax: void* malloc(size_t size)
Usage: int* p = (int*) malloc(5 * sizeof(int));
- calloc(): continuous allocation of n objects, each has
0
Syntax: void* calloc(n, size_t size)
Usage:int* p = (int*) calloc (5, sizeof(int))
- realloc(): Reallocates memory block of a previously allocated block
Syntax: void* realloc(void* p, size_t size)
Usage:int* pNew = (int*) realloc (p, 10 * sizeof(int)) // more memory was allocated, may not start from the same location
- free(): frees memory. Takes only one argument (pointer) since above functions implicitly store size information that
free()can read.
free(p);
Avoids memory leaks.
Tips
-
calloc()is justmalloc()followed bymemset()to0 -
we can free allocated memory by
free()or byrealloc(0, size) -
the above two are equivalent in outcome but not at all interchangeable because of optimization and surprises.
-
Other functions
- memset(): originally made for setting characters but can be used to set memory to only 0.
Syntax: void memset(void* ptr, int c, size_t size)
Usage: memset(arr, 0, sizeof arr);
File Management
A file is always terminated by an EOF character. And file functions check for this character often.
Operations
To open a file: fopen(const char* filename, const char* mode)
To read a file: fscanf() or fgets()
To write to a file: fputs() or fprintf()
To close a file: fclose(FILE* fp)
// Returns NULL if erorr
Checking end of file (returns non-zero value only if EOF is reached): int feof(FILE* fp)
Return file pointer position: long ftell(FILE* fp)
Going to specific position in file: void rewind(FILE* fp)
int fseek(FILE *fp, long int offset, int whence)
whence constants = SEEK_SET (beginning of file)
SEEK_CUR (current position of file pointer)
SEEK_END (end of file)
Set file pointer position: int fsetpos(FILE *fp, const fpos_t *position)
Rename file: int rename (const char *old_name, const char *new_name)
Remove file: int remove(FILE* fp)
Create temporary files: FILE *tmpfile(void)
// Perform file operations on it and closes automatically, no need to use fclose()
// rewind() can't tell if operation was a success or otherwise
fget/fput functions
int fgetc(FILE *pointer)
int fputc(int char, FILE *pointer)
char* fgets(char *str, int n, FILE *stream) //safer than gets() since it specifies maximum number of characters to be read
char* gets (char *str)
File Writing Modes

- Exclusive create-and-open mode (wx):
fopen()returnsNULLif file already exists or could not open.